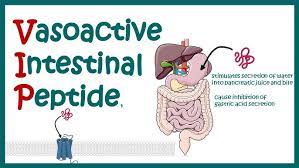
In reaction to eating, the small intestine secretes a vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) hormone. Blood sugar levels are maintained in check, and new cells are grown in the intestines by taking this supplement. Moreover, VIP acts as an anti-inflammatory and aids the immune system. Both VIP1 and VIP2 are peptides derived from the VIP molecule and have distinct purposes. VIP1 regulates blood sugar levels, while VIP2 encourages cell development and repair.
Neuroprotective benefits have also been found in VIP’s involvement in the gastrointestinal tract. It’s been demonstrated to help with memory and cognitive function and protect the brain from the effects of aging. Multiple health advantages, including enhanced blood sugar management, gastrointestinal health, and cognitive performance, may be achieved by VIP supplementation. More study is required, however, to corroborate these results.
A variety of physiological actions are carried out by Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP), also known as VPAC1. Pituitary Adenylate cyclase Activating Polypeptide (PACP) is structurally similar to the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Secreting hormones such as PACAP and VIP are the only ones known to be produced by invertebrates. VIP is found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, pancreas, and uterus. VIP is broadly dispersed throughout the body. Various factors, including food, stress, and inflammation, cause enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract to release VIP. Blood sugar levels, cell development, and repair in the stomach are controlled by vasoactive intestinal peptides (VIP). VIP is also known to have neuroprotective properties and help boost cognitive function and protect the brain from the degeneration that comes with growing older.
More study is required to prove the effectiveness of VIPs, which offers various potential advantages. The brain’s central nervous system (CNS) and its periphery are influenced by the neuropeptide known as vasoactive intestinal peptide. Structure-based comparisons show that VIP and PAC-activating polypeptides are structurally similar.
Patients with Alzheimer’s
A brain illness known as Alzheimer’s causes memory loss, cognitive decline, and mortality. In animal models of Alzheimer’s disease, VIP has been demonstrated to offer neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing benefits. Reduced amyloid-beta accumulation, increased learning and memory and protected neurons from death have been shown to be possible with VIP therapy. For Alzheimer’s disease therapy, VIPR1 activation may be a promising therapeutic target.
Cancer
Ovarian, pancreatic, and breast cancers have all benefited from VIP’s anti-cancer properties. Tumor development is inhibited, cell death is promoted, and cancer cell dissemination is reduced by VIP therapy. These findings imply that VIPR1 activation may be a viable therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a medical disorder in which blood sugar levels are abnormally high. In animal models of diabetes, VIP has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. In genetically obese mice, VIP therapy has also been proven to prevent the development of diabetes. Based on these results, activating VIPR1 may be a therapeutic target for the treatment of diabetes.
VIP and VIPR1 in Health and Illness
Many physiological systems are influenced by VIP and VIPR1. Blood sugar management, digestive health, cognitive function, and immunity have all been found to benefit from VIP use.
Diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease may benefit from VIPR1 as a therapeutic target. More studies need to confirm the effects of VIP and VIPR1 in humans. Buy VIP peptide if you are a researcher.